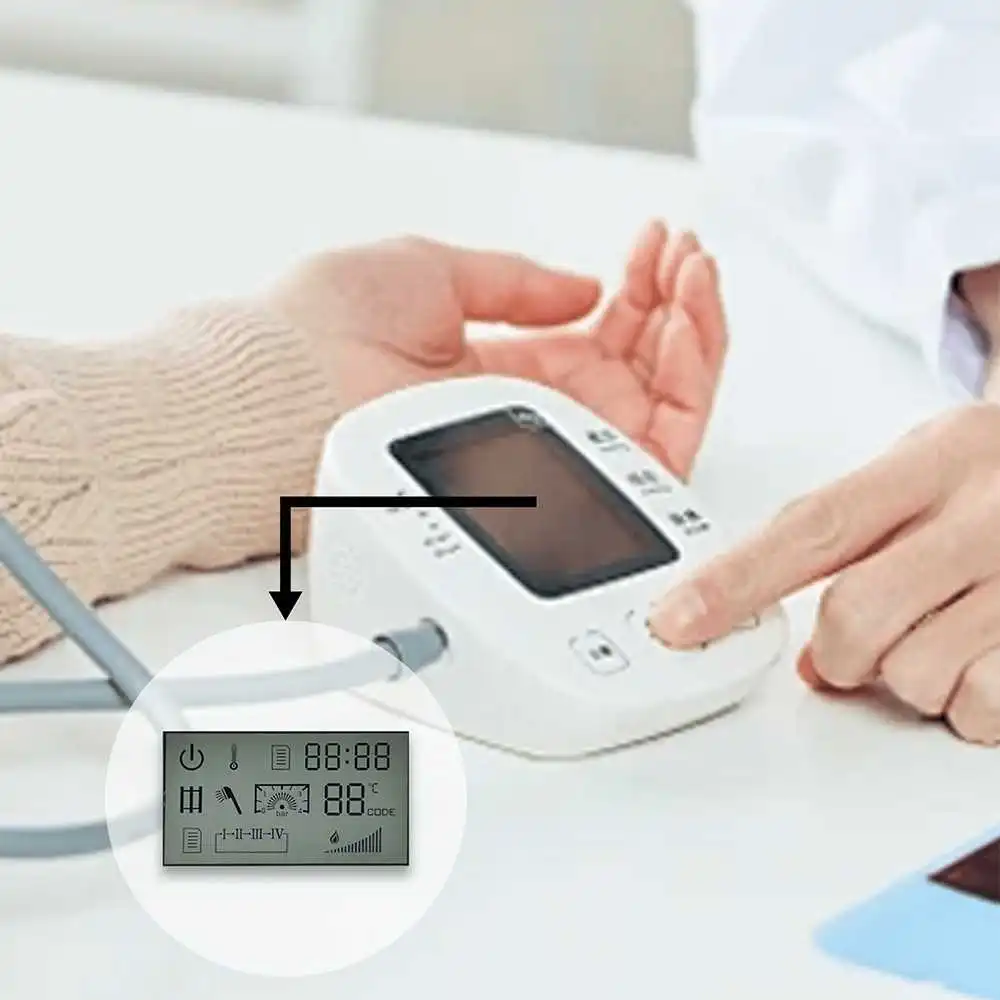
Monochrome
LCD Display
Simplicity and Clarity for
Focused Visuals
A monochrome LCD is a display technology that is usually used to display images or text in a single color. It consists of a liquid crystal layer, a glass substrate, a polarizer, and a drive circuit. Unlike a color L CD, a monochrome LCD can only display one color, usually monochrome, such as black, white, or other single colors.
Major Partners
LCD Structure
The LCD is composed of two pieces of glass with transparent electrodes (ITO electrodes) on top and bottom. The oriented liquid crystal is sandwiched between the electrodes. Then a polarizer is attached to the outside of the electrodes. This is the basic structure of the simplest LCD. On this basis, a driving circuit, connecting medium or backlight source can be added to form an LCD module.
Introduction
of Main Material LCD
Matter has three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Usually, when a solid is heated to its melting point, it will turn into a transparent liquid, and when it is heated further, it will turn into a gas. In 1888, when Reinitzer heated its solid crystal to 145 degrees, it melted into a liquid. The liquid is turbid, while all pure substances are transparent when melted. If it is heated to 175 degrees, it seems to melt again and become a clear and transparent liquid. Later, German physicist Lehmann called the turbid liquid in the middle zone a liquid crystal.
How Does LCD Work?
The liquid crystal molecules are arranged in a spiral shape inside the LCD box, twisted 90 degrees between the two surfaces (as shown below). When light passes through an unpowered LCD, it becomes polarized light after passing through the first layer of polarizer. When the polarized light passes through the inside of the LCD, it is affected by the spirally arranged liquid crystal molecules, and the polarization direction of the light rotates 90 degrees, which is exactly the same as the direction of the other layer of polarizer, and the light passes smoothly. (Note: The optical axes of the two polarizers are perpendicular to each other)
When the LCD electrodes are energized, the liquid crystal molecules rearrange themselves in the direction of the electric field and are no longer spiral-shaped. As a result, the polarized light no longer rotates and is unable to pass through when it reaches the second polarizer.
If you have the opportunity to hold a magnifying glass close to the LCD, you will find what is shown in the picture below. (The color here reflects the color of the color filter on the LCD)
We know that red, blue and green are the so-called three primary colors. Using these three colors, you can mix a variety of different colors. Many flat-panel displays use this principle to display colors. We divide the three RGB colors into three independent points, each with different grayscale changes, and then treat the three adjacent RGB display points as a basic display unit, that is, pixel. That is, one pixel can have different color changes.

What is the Specific Difference Between a Monochrome LCD Display and a Color LCD Display
Monochrome LCD screens and color LCD screens are two different types of display technologies. They have some differences in display effects, application scenarios and working principles.
There is a significant difference in display effects between monochrome and color. Monochrome LCD screens usually can only display one color, such as black and white, gray, or a single color, while color LCD screens can display a variety of colors, including basic colors such as red, green, and blue, so that they can present richer and more diverse images and video content
There are differences in the application scenarios of monochrome LCD screens and color LCD screens. Since they only display one color, monochrome LCD screens are usually used in some simple applications, such as e-readers, pedometers, thermometers, etc.; while color LCD screens are widely used in mobile phones, TVs, computer monitors and other devices and applications that need to display colorful content.
There are also some differences in the working principles of monochrome LCD screens and color LCD screens. LCD screens adjust the degree of light transmission by controlling the orientation of liquid crystal molecules, thereby realizing the display of images. In monochrome LCD screens, liquid crystal molecules have only one orientation, so they can only display one color. In color LCD screens, the orientation of liquid crystal molecules can be changed by regulating the electric field, so that images of different colors can be displayed.
There are also differences in production costs between monochrome LCD screens and color LCD screens. Since monochrome LCD screens only need to control one color, their production costs are lower; while color LCD screens need to control multiple colors at the same time, their production costs are higher; this is one of the reasons why monochrome LCD screens are more common in some simple applications, while color LCD screens are mainly used in high-end applications that require high-quality image display.
In addition, with the advancement of technology, new LCD screen technologies, such as quantum dot LCD screens and OLED, are also emerging and gradually replacing traditional LCD screen technologies in some applications. These new screen technologies have advantages in color performance, contrast, energy consumption, etc., which may have a certain impact on the market position of monochrome LCD screens and color LCD screens.

What Determines the Price of LCD Screens?
The price of LCD screen is determined by many factors. The following are some of the main factors that can affect the price of LCD screen.
Size and Resolution
The size and resolution of industrial LCD screens are one of the important factors that determine the price. Typically, larger screens and higher resolutions result in higher costs because more materials and technology are required to produce these screens.
Quantity and Customization Requirements
Ordering industrial LCD screens in large quantities can usually get lower prices. If there are customization requirements, such as special sizes, specific interfaces and appearance designs, this may increase the cost of production and adjustment, thus affecting the price.
Supply Chain and Material Costs
LCD prices are also affected by supply chain and material costs. Fluctuations in raw material prices and the profits of middlemen and distributors in the supply chain may also have an impact on the final price.
Market Supply, Demand and Competition
Market supply, demand and competition conditions will also have an impact on the price of LCD screens. Excess supply may cause prices to fall, while shortages or high demand may push prices up.
Application
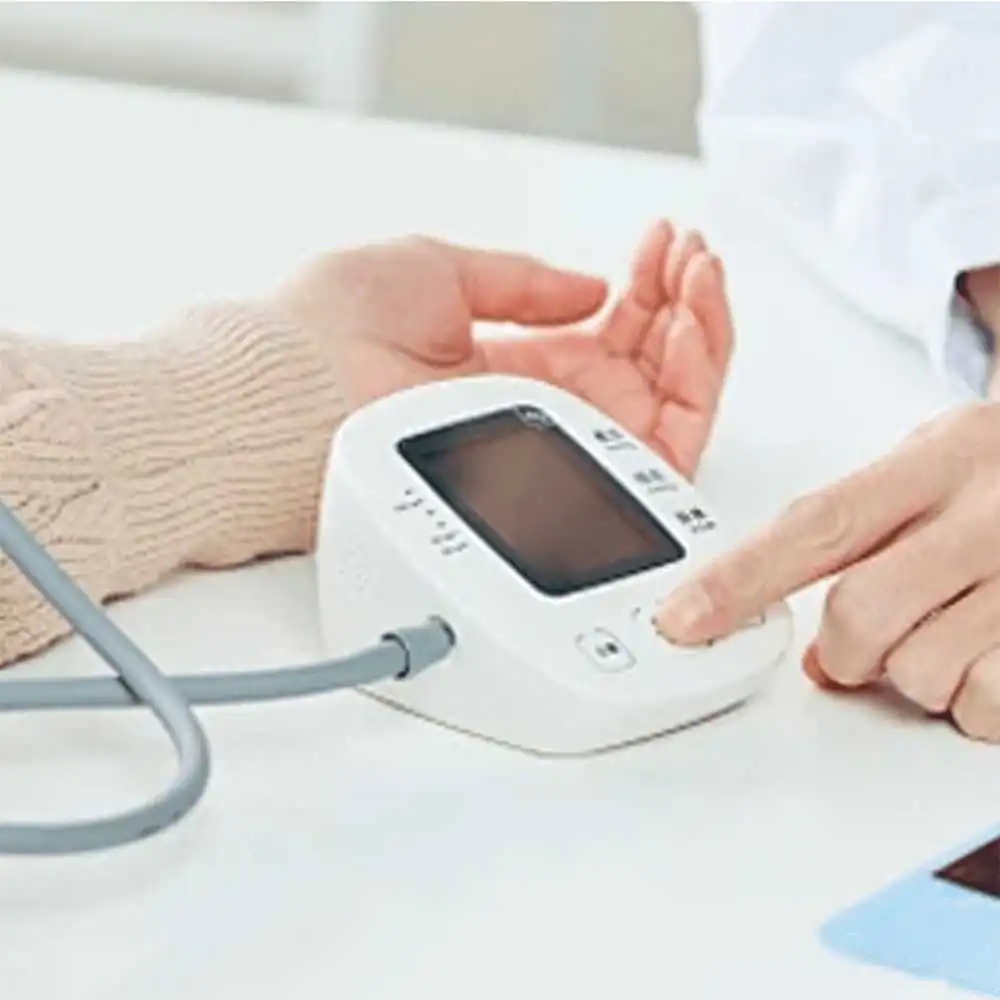
Our products are widely used in induction cookers, calculators, electric meters, hair curlers, car audio, thermostats, digital calipers, air conditioner remote controls, air conditioner fans, thermometers, blood pressure monitors, chargers, electronic scales, credit card machines, digital meters, gas dispensers, digital electric pens, water meters, rice cookers, safes, water heaters, massagers, steppers, radios, electronic watches, fax machines, etc. In the field of science and technology intelligence, the demand for product display is increasing rapidly.
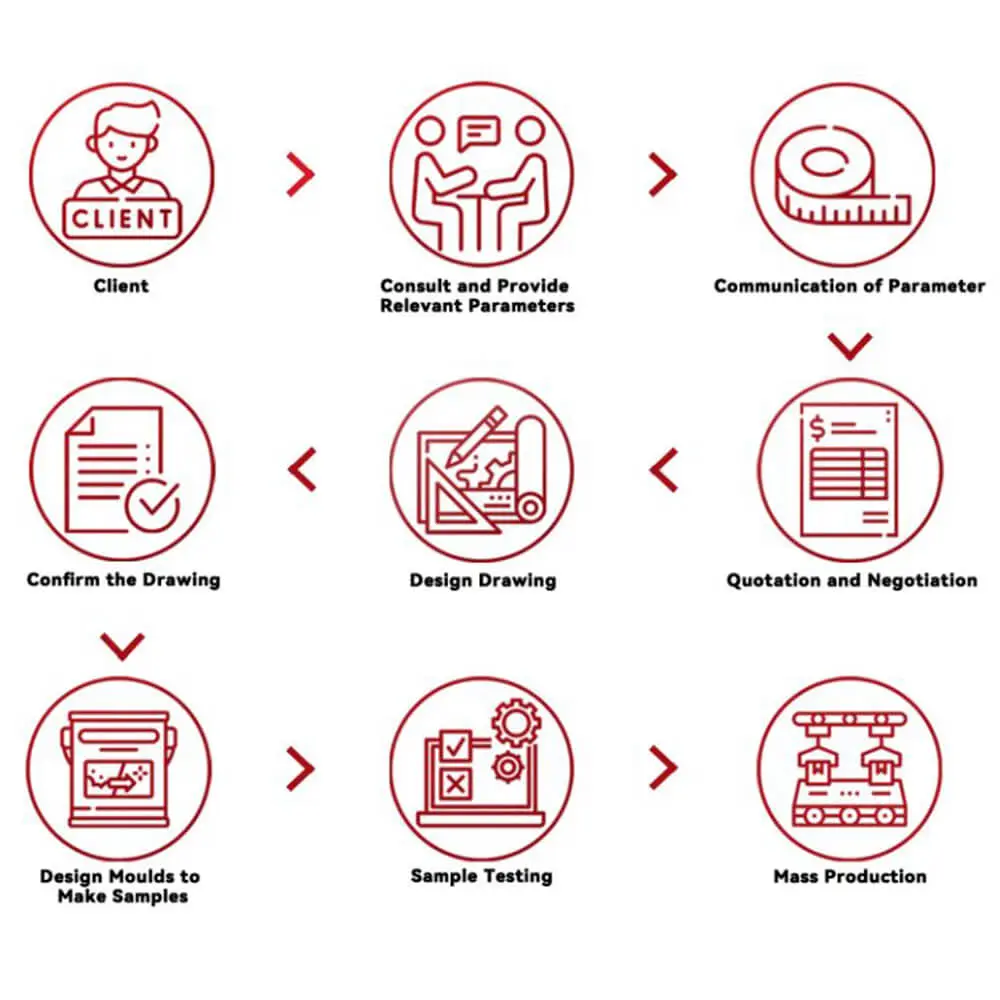
The Customization Parameters are as Follows
LCD Customization Notice
Please Provide the Parameters That Need to be Customized
Accept customization?
You are required to provide the length, width and thickness of the lcd screen glass.
What is the LCD display type?
Common display types are TN, VA, HTN, STN, and FSTN, which can be determined
based on your requirements.
What is the display mode?
Positive display – black characters on grey/white background
Negative display – white characters on black background
Blue film – white characters on blue background
Grey film – grey background, dark blue characters
Yellow and green film – yellow and green background, dark blue characters
What type of polarizer is?
Semi-transparent, fully transparent (backlight required), reflective (no backlight required).
What is the mode of conduction?
Conductive tape, hot press zebra paper, metal pin, FPC. According to customer requirements.
What is the angle of view?
Six o ‘clock, twelve o ‘clock, three o ‘clock, nine o ‘clock.
What is the driving mode and voltage?
Depending on the IC used, three parameters need to be known: duty, bias and voltage.
What is the operating temperature?
Normal temperature 0℃~50℃
Small wide temperature -10℃~60℃
Wide temperature -20℃~70℃
Super wide temperature -30℃~80℃
Get Started with Kaihang Display
Our engineering LCD design team is dedicated to promptly reviewing your information, identifying any gaps, and providing you with an accurate quote tailored to your specific display requirements. Simply fill out the form below or reach out to us via email.